What is Web Scraping?
Web scraping involves the action of fetching data from a web page and extracting it. This can be done by extracting information from the html elements of the webpage. The information extracted can then be formatted, searched and subsequently parsed into a database or spreadsheet for further analysis. Although this can be done manually, scraping generally involves the use of a script or bot to automate the process over hundreds to thousands of webpages.
Why Scrape the Web?
There are many reasons why web scraping is done, some examples include data collection from websites such as TripAdvisor, Yahoo Finance, PropertyGuru where there are no publicly available API’s for users to extract data. To manually copy out the data one page at a time is a very time-consuming process, so we turn to web scraping to retrieve the data that we need. The scraped data can then be used for data analysis or further processing for example informing users of any upcoming new events that can be added to their calendar.
In this example, I will be looking at how to scrape TripAdvisor to extract information to predict restaurant ratings based on TripAdvisor customer reviews.
Scraping Trip Advisor
For our example, we will be scraping for reviews of restaurants in Singapore that are on TripAdvisor. As I did this project in early 2020, at the time of writing this post, the information may not accurately reflect the TripAdvisor website layout at the point of the project.
Methodology
In order to scrape our target website, we first have to analyse the website and where our data that we want is stored. In our case, we want to extract the TripAdvisor reviews of each restaurant in Singapore. Looking at the TripAdvisor website, we would have to do the following:
- Go to the page listing restaurants in Singapore
- Go into each restaurant page and extract all the reviews related to the restaurant
- Store the information in a format to be processed later (e.g. DataFrame)
- Repeat
General Observations
- There are about 30 to 31 restaurants listed on each page for restaurant listings
- Not every restaurant has a review, for those that do, you would need to go through each individual review page to extract the reviews.
Note: There are websites that do have anti-scraping mechanisms in place, such as blocking your IP address when there are too many requests in a short period of time
Taking a general look at the number of reviews each restaurant has, higher ranked restaurants have over 1000 reviews, with lower ranked restaurants having fewer reviews. Taking a conservative estimate that each restaurant has an average of 100 reviews, multiplied by the total number of restaurants, the amount of time taken to scrape will be quite substantial.
Therefore in order to speed things up, we will scrape in parallel (multi-threading).
What Do We Need?
In order to scrape and extract the data, we will be using the following python packages:
- Selenium: Allows browser automation
- beautifulsoup4: Parses in the HTML page source to extract data
- webdriver-manager (optional) : Automates webdriver version that will be used for Selenium
Installation
pip install selenium
pip install bs4
pip install webdriver-manager
Importing Packages
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
How To Do It
This can be done by going to the webpage of interest and inspecting the web elements where we want to extract the information. This can be done by accessing the developer tools of Chrome/Edge by hitting the F12 key on your keyboard for both Windows and MacOS.
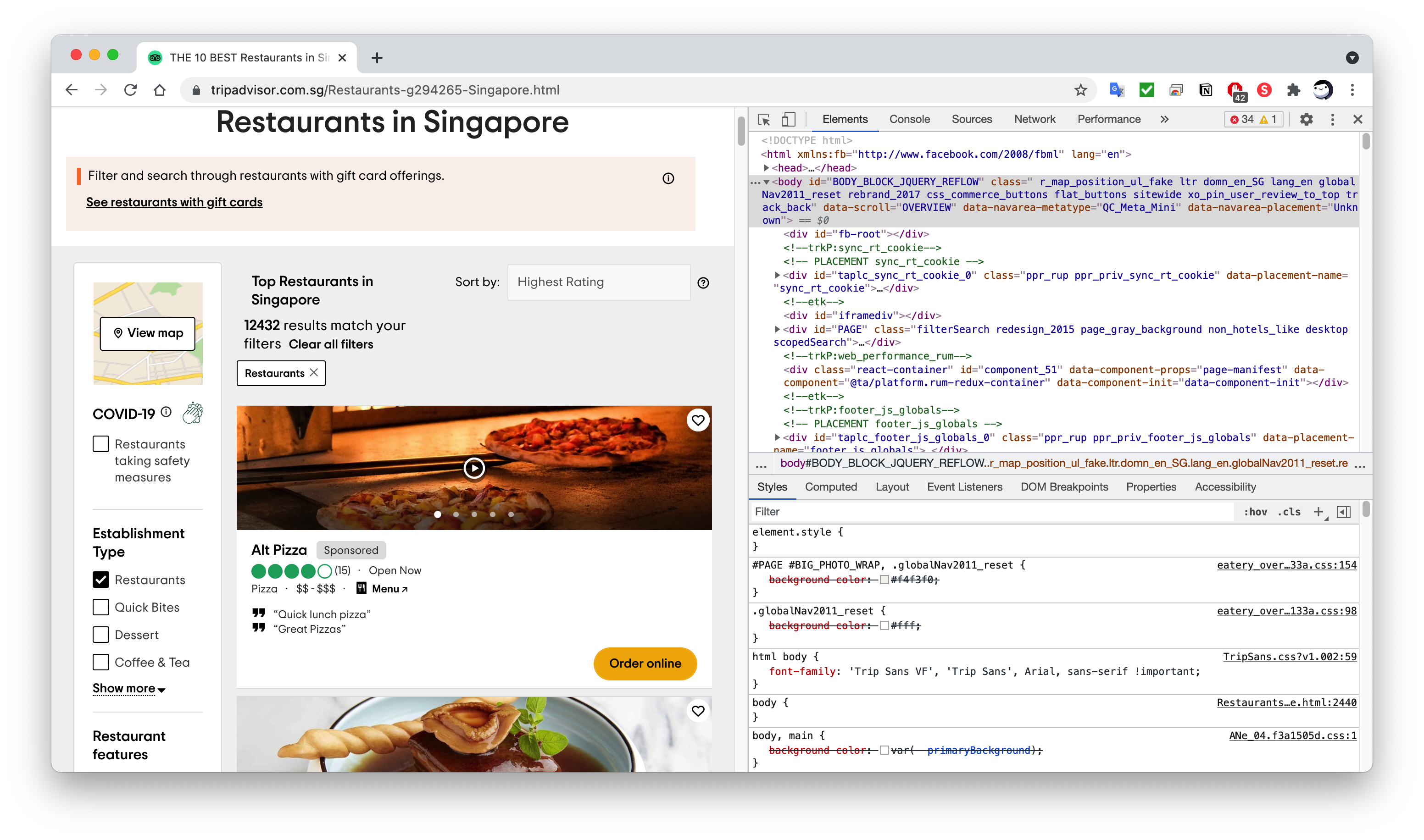
Getting Restaurant URLS
In order to scrape the reviews, we will first extract the restaurant URLs to be stored for later use. In order to do this, we will cycle through each page of restaurant listings and retrieve the url links of each restaurant together with the restaurant name. Ending with this DataFrame:
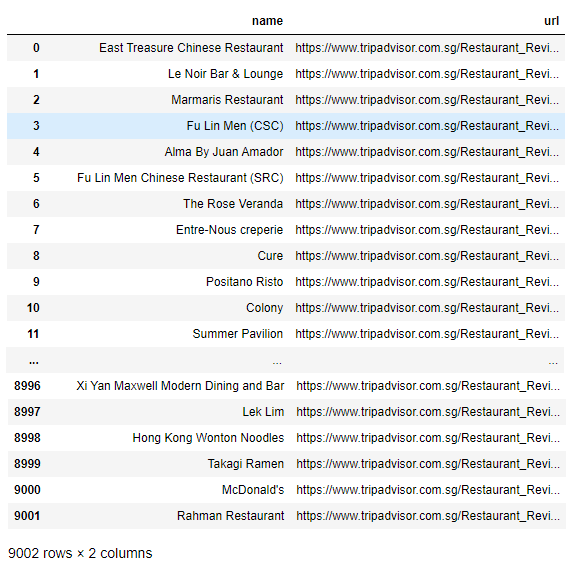
Getting the Reviews
Once we’ve got the list of URLs, next we need to scrape the reviews from each of the restaurants page. This is done through multi-threading in order to scrape 9000 restaurants. Ending with this DataFrame:
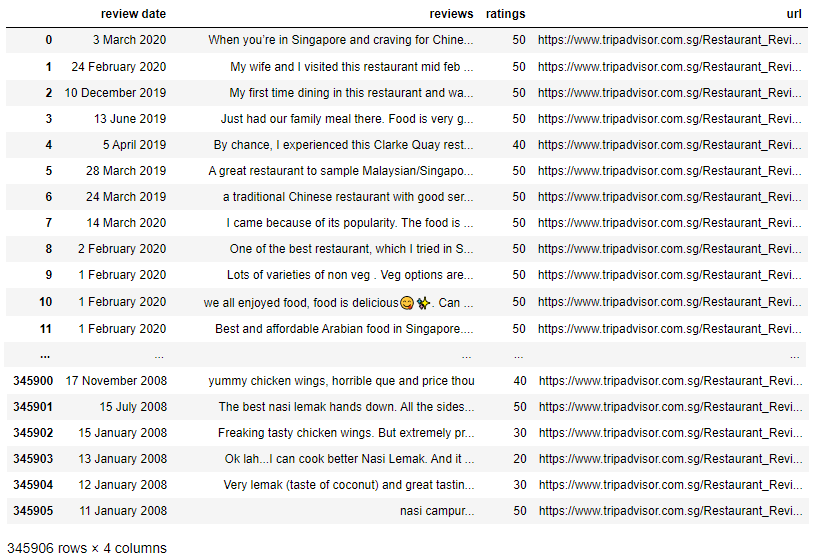
Multithreading
In order to speed up the time to scrape 9000+ restaurants, Multithreading will be used to run 5 browsers concurrently, effectively cutting the scrape time by a factor of 5.
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
restaurant_reviews = []
start = time.time()
futures = [executor.submit(get_Reviews_multithread, links) for links in urls]
for result in as_completed(futures):
restaurant_reviews.append(result)
end = time.time()
Explanation of the code:
- ThreadPoolExecutor is launched with a maximum 5 workers (tasks are split into 5 threads)
- Instantiate a empty list containing restaurant reviews
-
futures is a list comprehension expressing how many times you want
executor.submit(get_Reviews_multithread, links)to be run. If a list comprehension is not used, the code would look like this: - Example code without list comprehension
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor: executor.submit(get_Reviews_multithread, "restaurant_1_url") executor.submit(get_Reviews_multithread, "restaurant_2_url") executor.submit(get_Reviews_multithread, "restaurant_3_url") executor.submit(get_Reviews_multithread, "restaurant_4_url") executor.submit(get_Reviews_multithread, "restaurant_5_url") # and so on... for all URLS - The method
as_completedreturns the results of each thread. In this case, it returns a list of all the reviews and we then append them to the empty list ofrestaurant_reviews
Final Thoughts
Web Scraping is an extremely useful skill in Data Extraction as not every website will have a publicly available API for use to download information. In such instances we turn to Web Scraping to extract the information from the web to perform analysis. This can be extremely useful for Financial Analysts as they have to gather information from multiple sources on a routine / periodic basis to provide insights and updates of companies to invest in.